3 Possible Scenarios When The 21 Million Bitcoins Are Mined
An attempt to answer a question that will become essential for Bitcoin in the years to come.
All those with an interest in Bitcoin have understood that the maximum quantity of Bitcoins that can be put into circulation is 21 million.

This arbitrary boundary was defined by Satoshi Nakamoto when he designed the Bitcoin Blockchain.
New Bitcoins Are Issued Via Mining
To function properly, the Bitcoin Blockchain requires users to become nodes of the network and make their computing power available to validate blocks of transactions.
This computing power is used to solve the famous mathematical puzzle that underlies the Bitcoin consensus algorithm, the Proof-Of-Work.
When designing the Bitcoin Blockchain, Satoshi Nakamoto looked for a way to encourage individuals to become nodes in order to maximize network security. Indeed, the more computing power available on the network, the more difficult it is to hack into the network via a takeover attack of 51% of the computing power.
The Bitcoin Reward Is An Incentive
To incentivize users to make their computing power available to the Bitcoin Blockchain and thus secure the network, Satoshi Nakamoto has set up a Bitcoin reward mechanism.
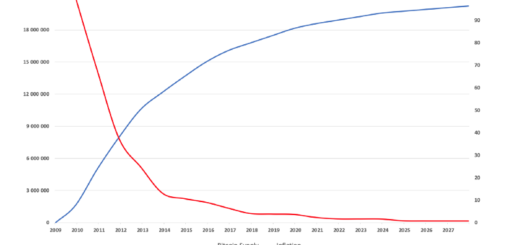
Thus, new Bitcoins are created when a block of transactions is validated in what is usually called mining. Currently, when a block of transactions is validated, the miners who have performed this validation will share a reward of 12.5 BTC.
Every 210,000 validated blocks of transactions, the Bitcoin Blockchain automatically divides the amount of this reward by two. This is better known as Bitcoin Halving. In May 2020, after the block 630,000, the Blockchain Bitcoin will perform its third Halving with the reward going from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC.
Similarly, after the block 840,000, approximately in 2024 at the current pace, another Halving will take place, dropping the reward to 3.125 BTC per block of validated transactions.
In the future, the number of new Bitcoins created will become inexorably scarce.
In addition to this famous reward, miners are paid via transaction fees, the amount of which is currently much lower than this reward.
Will Transaction Fees Be Sufficient To Incentivize Miners?
As the Bitcoin reward allocated to miners validating a block of transactions decreases, some predict a significant increase in transaction fees.
Why? Quite simply because miners will have to find a new financial incentive to make their computing power available to the Blockchain Bitcoin.
With transaction fees rising sharply, it would then become almost impossible to use Bitcoin as a means of payment or a medium of exchanges.
Bitcoin could become just a store of value with users favoring holding BTC over transacting BTC.
This is what is currently happening since many people prefer to accumulate Bitcoins by betting on its high volatility in order to make good profits in the years to come.
However, in order to prevent transaction fees from becoming too high and for miners to continue to secure the Bitcoin network in a profitable way, there is a solution:
With mass adoption by the general public of Bitcoin as a mean of payments or a medium of exchanges, the volume of transactions would become so large that even reduced transaction fees would be sufficient to incentivize miners to make their computing power available to secure the network.
A Problem That May Centralize The Bitcoin Blockchain
In the event that the Blockchain Bitcoin does not reach a sufficiently large number of users, the volume of transactions will not be sufficient for miners to continue their work while maintaining reduced transaction fees.
In fact, more and more miners would be tempted to leave the Bitcoin Blockchain and make their computing power available to other Blockchains, for example.
A mass departure of many miners would necessarily imply a reduction in their number, which would reinforce the centralization of the Bitcoin Blockchain.
The security of the network would then rest in the hands of a limited number of actors, which is a significant risk for Bitcoin.
3 Possible Scenarios For The Future Of Bitcoin
The last Bitcoin will be mined in 2140, after which date the reward will fall below 1 Satoshi, which will be negligible compared to current rewards.
As guarantors of the security of the Blockchain Bitcoin, the miners will have to find another interest to make their computing power available to the network. From that moment on, I see three main possible scenarios:
- Transaction fees will skyrocket, turning Bitcoin only as a store of value with a much more centralized network than today due to a smaller number of miners.
- A mass adoption by the general public of Bitcoin as a means of payment or as a medium of exchange will make it possible to have such a large volume of transactions that it will remain interesting for miners to validate blocks of transactions while guaranteeing reduced transaction fees.
- The Bitcoin Core developer community will be able to find a solution to solve this potential problem, which will become more and more important in the coming years following the upcoming Halvings.
For my part, scenario 2 seems quite possible to me . If adoption is delayed, I also have full confidence in the Bitcoin Core developer community to find solutions in the future that will allow Bitcoin to continue its progress despite the gradual disappearance of the reward when a block of transactions is validated.